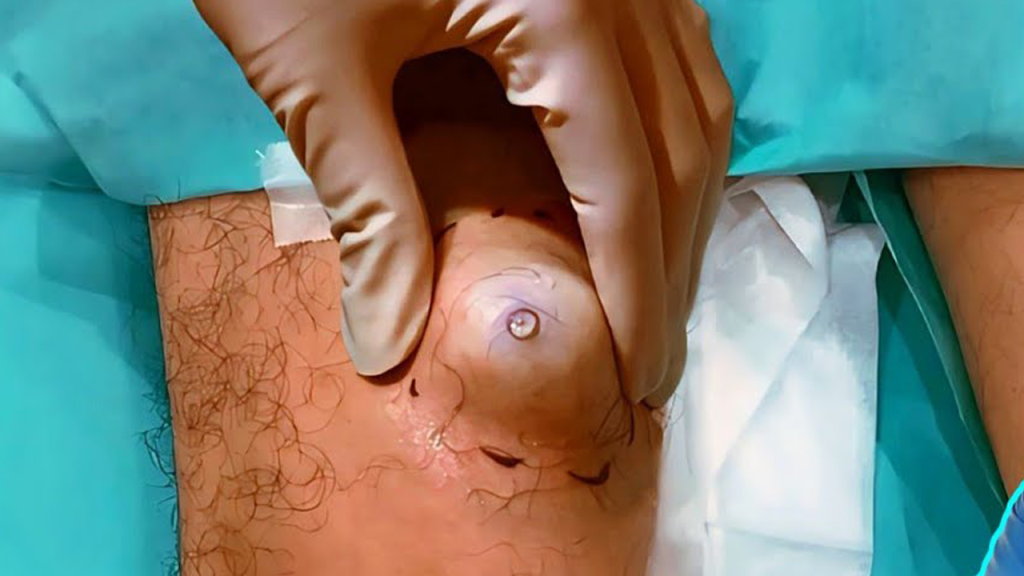
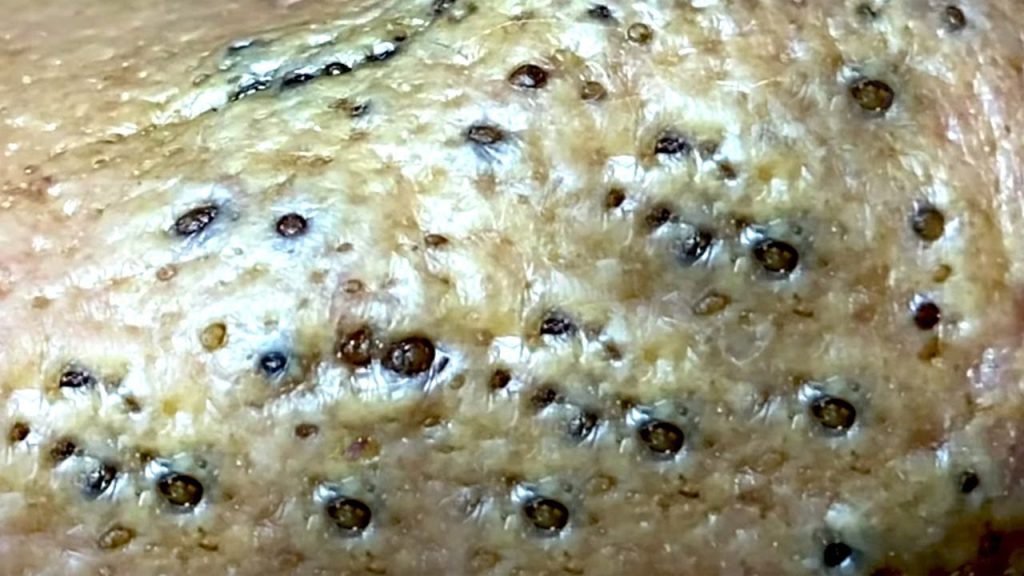
Sebaceous cysts are benign lumps that form under the skin when sebaceous glands or hair follicles become blocked. These cysts are commonly found on the face, neck, or upper body but can also appear behind the thigh. While generally harmless, they can grow large and cause discomfort, especially if irritated or infected.
Causes of Sebaceous Cysts
Sebaceous cysts form due to:
- Blocked sebaceous glands caused by trauma or clogged pores.
- Skin injuries or irritation.
- Genetic conditions that predispose individuals to cyst formation.
Symptoms of a Sebaceous Cyst
- A round, firm lump beneath the skin.
- It is usually painless unless infected, in which case it may become red, swollen, and tender.
- Infected cysts may leak a foul-smelling, cheese-like substance.
Treatment Options
While some sebaceous cysts resolve on their own, larger or bothersome cysts may require medical intervention:
- Drainage: A minor incision allows the cyst to drain. However, the sac remains, increasing the chance of recurrence.
- Surgical Removal: This ensures complete removal of the cyst and its sac, reducing recurrence risk.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed if the cyst is infected or inflamed.
Aftercare
- Keep the wound clean and dry.
- Follow medical instructions for dressing and care.
- Watch for infection signs, such as increasing redness or discharge.
Sebaceous cysts are generally not serious but can cause discomfort, especially in high-friction areas like the back of the thigh. Seek medical advice if the cyst grows, becomes painful, or shows signs of infection.