Comments Off on Understanding a Dental Abscess
Types:
- Periapical Abscess: Forms at the tip of the tooth root, usually due to tooth decay or trauma.
- Periodontal Abscess: Develops in the gums, often due to gum disease.
- Gingival Abscess: Forms in the gum tissue without affecting the tooth or its supporting structures.
Common Symptoms:
- Severe, throbbing toothache
- Sensitivity to hot and cold
- Swelling in the gums, face, or jaw
- A foul taste or smell in the mouth if the abscess bursts
- Fever or swollen lymph nodes in severe cases
Treatment Options
1. Immediate Relief (Temporary Measures):
- Rinse with Warm Salt Water: Mix 1/2 teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water to reduce swelling and draw out pus.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Use ibuprofen or acetaminophen to manage pain and inflammation.
- Cold Compress: Apply to the outside of your cheek to reduce swelling.
2. Professional Dental Treatment:
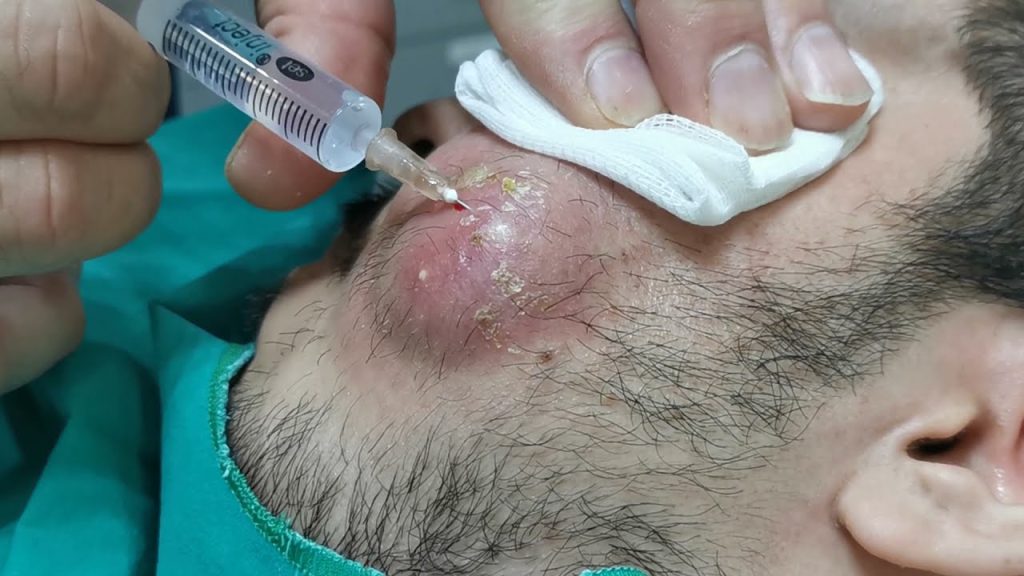
- Drainage of the Abscess: The dentist will make a small incision to drain the pus and relieve pressure.
- Root Canal Treatment: If the abscess stems from the tooth’s pulp, the dentist will remove the infected tissue and seal the tooth.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, it may be removed to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to control the infection, especially if it has spread beyond the tooth.
3. Aftercare:
- Keep the treated area clean by rinsing with salt water or using a prescribed mouthwash.
- Follow your dentist’s instructions regarding diet and oral care.
Preventing Dental Abscesses
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss regularly.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings.
- Avoid excessive sugary foods and drinks.
- Address dental issues, such as cavities or gum disease, promptly.
When to Seek Emergency Care
A dental abscess can lead to severe complications like spreading infection, sepsis, or difficulty breathing or swallowing. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
-
-
- High fever
- Rapidly increasing swelling
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Severe pain that doesn’t improve with pain relievers
-